How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a structured approach to mastering drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and legal considerations. We’ll explore the nuances of flight principles, camera settings, and essential maintenance procedures, ensuring you’re well-equipped to take to the skies responsibly.
Understanding the intricacies of drone technology, coupled with a commitment to safety and legal compliance, will empower you to harness the full potential of your drone. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the world of drone piloting with ease and proficiency.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight inspection is crucial for ensuring both the safety of your drone and those around you. This involves checking various components and verifying that environmental conditions are suitable for flight.
Pre-Flight Inspection Steps
- Battery Check: Verify the battery level is sufficient for the planned flight time, and ensure the battery is properly connected and securely fastened.
- Propeller Inspection: Examine each propeller for cracks, damage, or imbalances. Replace any damaged propellers.
- GPS Signal Strength: Confirm a strong GPS signal is acquired before takeoff. A weak signal can lead to inaccurate positioning and potential crashes.
- Gimbal Check (if applicable): If your drone has a gimbal, ensure it’s properly calibrated and functioning correctly.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a thorough visual inspection of the drone’s body for any damage or loose parts.
- Environmental Check: Assess wind conditions, visibility, and airspace restrictions before takeoff.
- Calibration: Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) according to the drone’s manufacturer instructions.
Pre-Flight Checklist Table
| Checklist Item | Inspection Method | Acceptable Result | Unacceptable Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Check battery indicator | Above 20% (or as per manufacturer recommendation) | Below 20% (or as per manufacturer recommendation); damaged battery |
| Propeller Integrity | Visual inspection | No cracks, bends, or damage | Cracks, bends, or any visible damage |
| GPS Signal Strength | Check GPS indicator on controller | Solid GPS lock with sufficient satellites | Weak or no GPS signal |
| Gimbal Function (if applicable) | Manually move the gimbal | Smooth and responsive movement | Jerky movement, unresponsive, or visible damage |
Safe Launch and Landing Procedures

Launching and landing a drone safely requires a calm and controlled approach. Improper techniques can lead to damage or accidents.
- Find a safe, open area away from obstacles and people.
- Ensure the drone is properly calibrated and has a strong GPS signal.
- Slowly increase throttle to lift off vertically.
- Maintain a stable altitude and avoid sudden movements.
- For landing, slowly decrease throttle until the drone gently touches down.
- Power off the drone after landing.
Drone Controls and Navigation: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding the basic controls and various flight modes is fundamental to safe and effective drone operation. Different controllers offer varying levels of control and features.
Basic Drone Controls
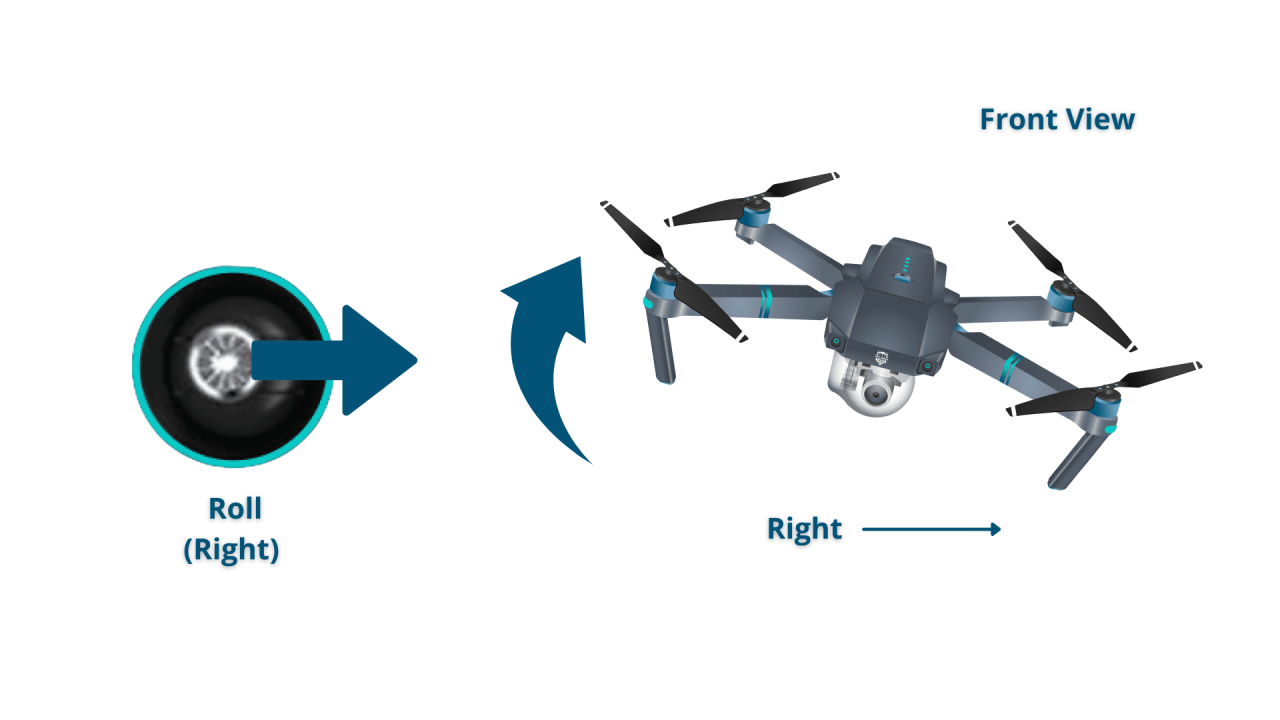
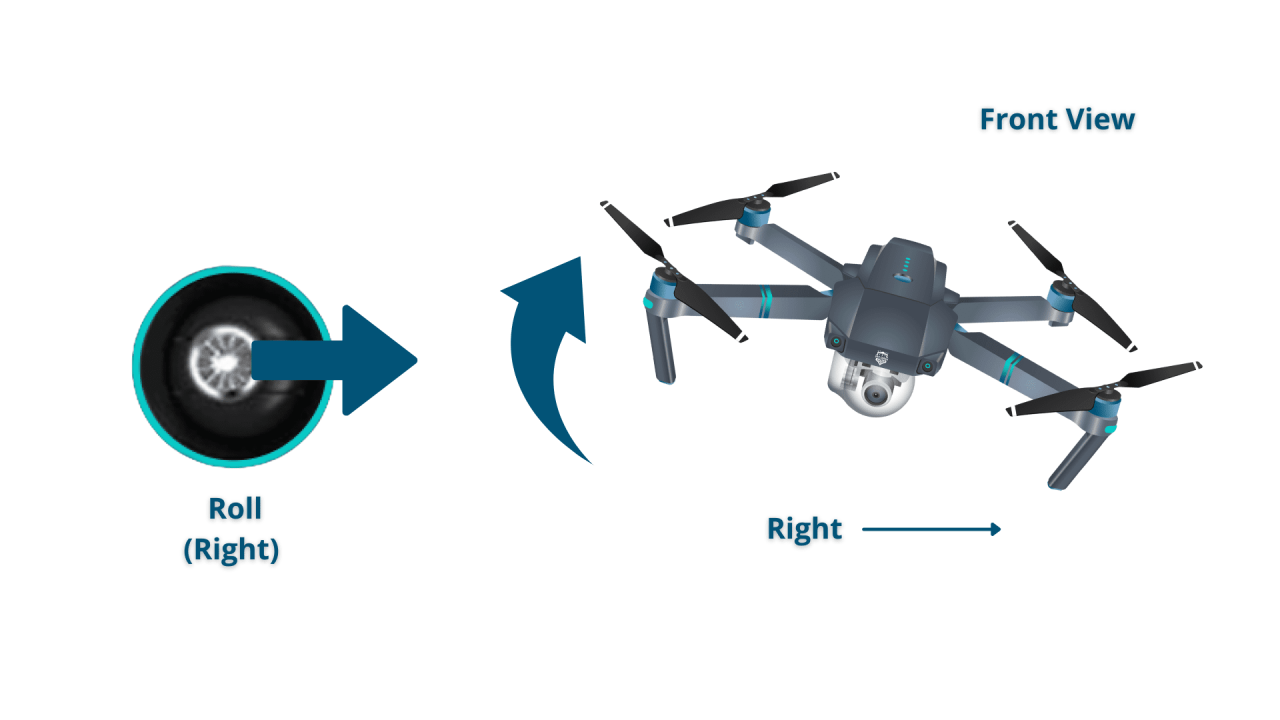
Most drones utilize a controller with sticks to manage throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll. Throttle controls altitude, yaw rotates the drone left or right, pitch tilts the drone forward or backward, and roll tilts the drone left or right.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering all these essential elements, you should check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone and improve your piloting skills. Ultimately, responsible drone operation ensures safe and enjoyable flights.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight scenarios. Beginner mode limits speed and responsiveness, while Sport mode offers increased maneuverability. Manual mode provides full control but requires significant skill.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness, ideal for beginners.
- Sport Mode: Offers increased maneuverability and speed.
- Manual Mode: Provides full control over all aspects of flight, requiring advanced skills.
Drone Controller Types
Drone controllers range from traditional joysticks to smartphone apps. Joysticks provide more precise control, while smartphone apps offer intuitive interfaces, often with automated features.
Navigating to a Specific Location
Precise navigation requires a combination of visual cues, GPS data, and controller inputs. The process usually involves setting a waypoint or using GPS coordinates.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires understanding regulations and best practices, and for a comprehensive guide on all aspects of safe and responsible flight, you should consult a resource like this one: how to operate a drone. This will help you build the skills necessary to operate a drone confidently and safely.
- Identify the target location.
- Set the drone’s GPS coordinates to the target location (if the drone supports this feature).
- Manually pilot the drone towards the target location, using visual cues and GPS data to guide you.
- Adjust the drone’s position as needed to maintain accuracy.
- Once at the target location, adjust the camera angle to capture the desired shot.
Understanding Drone Flight Principles
Understanding fundamental flight principles enhances your ability to control the drone effectively and safely, especially in challenging conditions.
Center of Gravity
The center of gravity (CG) is the point where the drone’s weight is evenly balanced. Maintaining a balanced CG is crucial for stability and preventing unwanted movements.
Wind Effects
Wind significantly impacts drone stability and flight path. Strong winds can push the drone off course, requiring adjustments to maintain position. Pilots should always check weather conditions before and during flight.
Altitude and Obstacle Avoidance
Maintaining a safe altitude and distance from obstacles is paramount to prevent collisions. Always be aware of your surroundings and use the drone’s obstacle avoidance features (if available).
Smooth Drone Maneuvering
Smooth and controlled maneuvers are achieved through gradual and precise adjustments to the controls. Avoid sudden movements that can destabilize the drone, especially in windy conditions.
Photography and Videography with a Drone
Capturing stunning aerial imagery requires understanding camera settings and employing creative composition techniques. Experimentation is key to developing your own style.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Optimizing camera settings is crucial for achieving high-quality images and videos. Understanding ISO, shutter speed, and aperture is essential.
Camera Angles and Shots
Drones allow for unique camera angles and shots impossible with traditional methods. Experiment with different perspectives to add visual interest.
- Overhead Shots: Provide a bird’s-eye view of the scene.
- Tracking Shots: Follow a moving subject.
- Orbiting Shots: Circle around a subject.
- Low-Angle Shots: Create dramatic perspectives.
Tips for Compelling Aerial Photography and Videography
- Plan your shots carefully.
- Use the “rule of thirds” for composition.
- Pay attention to lighting conditions.
- Experiment with different camera angles and movements.
Camera Setting Table
| Camera Setting | Description | Use Case | Example Image Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO | Measures the sensitivity of the camera sensor to light. | Low ISO for bright conditions, high ISO for low-light conditions. | A low ISO image of a sunlit landscape shows vibrant colors and sharp details; a high ISO image of a nighttime cityscape shows some noise but captures the city lights effectively. |
| Shutter Speed | The length of time the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. | Fast shutter speed for freezing motion, slow shutter speed for motion blur. | A fast shutter speed image of a waterfall shows the water frozen in mid-air; a slow shutter speed image of a waterfall shows smooth, flowing water. |
| Aperture | Controls the amount of light entering the camera. | Wide aperture for shallow depth of field, narrow aperture for deep depth of field. | A wide aperture image of a flower has a blurred background, focusing attention on the flower; a narrow aperture image of a landscape has everything in sharp focus from foreground to background. |
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are crucial for prolonging the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued safe operation.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule ensures optimal performance and longevity. This includes cleaning, inspecting, and storing the drone properly.
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the drone’s body and propellers to remove dirt and debris.
- Inspection: Inspect the drone for any signs of damage or wear and tear after each flight.
- Storage: Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes

Understanding common malfunctions and their causes allows for quicker troubleshooting and resolution.
- Low Battery: Insufficient charge, damaged battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Obstructions, interference, weak signal.
- Motor Problems: Damaged motor, loose connections.
Troubleshooting Steps
Systematic troubleshooting ensures efficient problem resolution.
- Low Battery: Charge the battery, replace if necessary.
- GPS Signal Loss: Move to an open area, restart the drone.
- Motor Problems: Inspect motors for damage, check connections.
Replacing Drone Components
Replacing components such as propellers and batteries requires careful attention to ensure proper installation and safety.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and adhering to local drone laws and regulations is essential for responsible and legal drone operation. These regulations vary by location.
Relevant Laws and Regulations, How to operate a drone
Before flying, research and understand all relevant laws and regulations in your area. These laws often include registration requirements, airspace restrictions, and operational guidelines.
Permits and Licenses
Depending on the type of drone operation and location, obtaining necessary permits and licenses may be required. Check your local aviation authority for specific requirements.
Restrictions on Drone Flights
Many areas have restrictions on drone flights near airports, crowded areas, and private property. Always respect these restrictions to ensure safety and compliance.
Key Legal Considerations
- Register your drone (if required).
- Obtain necessary permits and licenses.
- Respect airspace restrictions.
- Maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Do not fly over people or crowds.
- Do not fly near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Obtain permission before flying over private property.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Once comfortable with basic operation, you can explore advanced flight maneuvers and techniques for more creative and complex shots.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers like flips, rolls, and precision hovering require practice and skill. Always practice in a safe and open area.
Waypoint Navigation and Automated Flight Planning
Waypoint navigation allows you to program a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously. Automated flight planning software simplifies this process.
Cinematic Aerial Shots
Achieving cinematic aerial shots involves careful planning, smooth movements, and creative camera angles. Practice is essential for mastering these techniques.
Performing a Specific Advanced Maneuver: 360-Degree Orbit
A 360-degree orbit involves circling a subject while maintaining a consistent altitude and distance. This requires precise control of the yaw and throttle.
- Position the drone at a safe distance from the subject.
- Maintain a constant altitude.
- Slowly and smoothly rotate the drone using the yaw control, completing a full 360-degree circle.
- Maintain consistent speed and distance throughout the maneuver.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of pre-flight procedures, flight controls, aerial photography techniques, maintenance practices, and legal regulations. By diligently following these guidelines and continuing to practice, you can confidently and responsibly explore the exciting world of drone technology. Remember that continuous learning and adherence to safety protocols are paramount for a successful and enjoyable drone piloting experience.
Detailed FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for drones with intuitive controls and flight modes designed for ease of use.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
Charge your drone battery after each flight and avoid fully depleting it. Refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for optimal charging practices.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately bring it down to a safe landing. Avoid attempting complex maneuvers without a stable GPS connection.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and registration procedures.
What is the best way to clean my drone?
Use a soft, dry cloth to gently wipe down the drone body. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific cleaning recommendations.